
What is the Linux kernel?
The Linux kernel is the core component of the Linux operating system. It manages system resources, such as the CPU, memory, devices, and provides essential services for other software to run on top of it.
What is a shell in Linux?
A shell is a command-line interpreter that allows users to interact with the Linux operating system. It interprets user commands and executes them. The shell also provides features like scripting, automation, and access to various system utilities.
How do you find files in Linux?
The find command is commonly used to search for files in Linux. You can specify the starting directory and various search criteria such as filename, size, permissions, and modification time. For example, find /path/to/search -name "filename" will find files with the specified name within the given directory.
What is the difference between Linux and Unix?
Linux and Unix are both operating systems, but they have different origins. Unix refers to a family of operating systems that share similar principles and design concepts. Linux, on the other hand, is an open-source operating system kernel inspired by Unix. While Linux is Unix-like, it is not a certified Unix system.
What is the difference between a process and a thread in Linux?
A process is an instance of a running program that has its own memory space and resources. It is managed by the kernel and can consist of multiple threads. Threads, on the other hand, are lightweight execution units within a process. They share the same memory space and resources of the parent process.
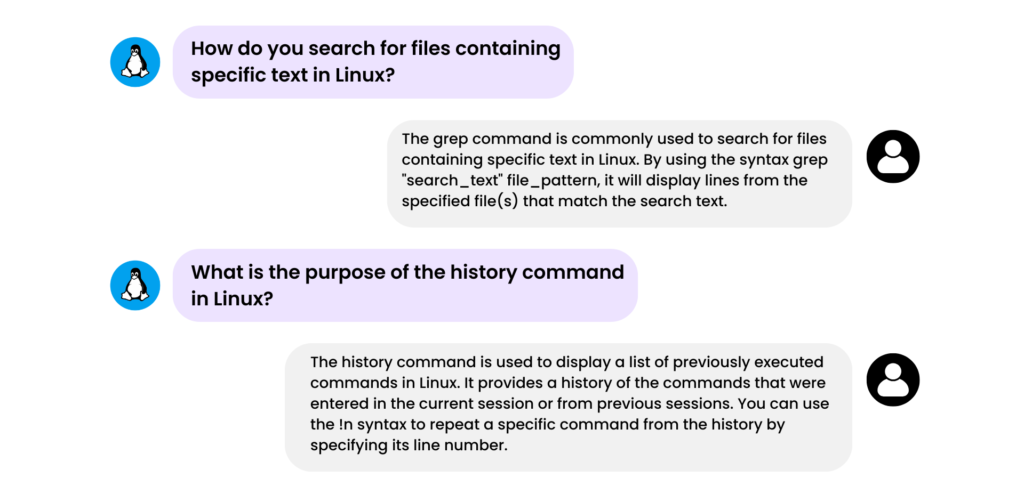
What is the purpose of the grep command?
The grep command is used to search for specific patterns or regular expressions within text files or command output. It can be combined with other commands using pipes (|) to perform powerful text processing operations.

Explain the use of the chmod command.
The chmod command is used to change the permissions (read, write, execute) of files and directories in Linux. It can be used to grant or revoke permissions for the owner, group, and others. The permissions can be represented in either symbolic (e.g., chmod u+r file) or octal notation (e.g., chmod 644 file)
What is a symbolic link in Linux?
A symbolic link, also known as a symlink or soft link, is a special type of file that acts as a pointer to another file or directory. It provides a convenient way to reference files or directories located elsewhere in the filesystem. Symbolic links can be created using the ln -s command.
How do you check system resource usage in Linux?
The top command is commonly used to monitor system resource usage in real-time. It displays information about CPU usage, memory usage, running processes, and more. Additionally, the free command provides information about memory usage, while the df command shows disk space usage.
Explain the role of the /etc/passwd file
The /etc/passwd file is a system file in Linux that stores user account information. Each line in the file represents a user and contains details such as the username, user ID (UID), group ID (GID), home directory, and default shell. However, modern Linux systems typically use /etc/shadow for password storage.
How do you check the network connectivity in Linux?
The ping command is commonly used to check network connectivity. By specifying an IP address or domain name, ping sends ICMP echo requests to the target and waits for replies. It helps determine if a host is reachable on the network.
How do you start, stop, and restart services in Linux?
The specific commands can vary depending on the Linux distribution, but commonly used commands are systemctl start
What is the purpose of the cron utility?
The cron utility allows scheduling and automating recurring tasks in Linux. It uses cron jobs, which are commands or scripts that run at specified intervals or times. The crontab command is used to manage and configure the cron jobs for individual users.
How do you manage software packages in Linux?
Linux distributions use package managers to manage software packages. Common package managers include APT (used by Debian and Ubuntu), YUM (used by Fedora and CentOS), and Pacman (used by Arch Linux). These package managers allow you to install, update, and remove software packages with ease. password storage.

How can you secure a Linux server?
There are several measures you can take to secure a Linux server:
• Keep the system up to date with security patches and updates.
• Use strong and unique passwords for user accounts.
• Implement a firewall to control network traffic.
• Disable unnecessary services and ports.
• Utilize secure protocols, such as SSH for remote access.
• Regularly monitor logs and audit system activities.
How do you create a backup in Linux?
There are various ways to create backups in Linux. One common method is using the tar command to create compressed archive files. For example, to create a backup of a directory, you can use the command tar -czvf backup.tar.gz /path/to/directory. There are also dedicated backup utilities like rsync and borgbackup available.
Explain the use of the ssh command.
The ssh command is used to establish secure shell connections to remote systems. It provides encrypted communication and allows you to log in to remote machines, execute commands remotely, and transfer files securely between systems. The command syntax is ssh username@hostname.
How do you monitor system performance in Linux?
Linux offers various tools to monitor system performance. Some commonly used tools include top, htop, and glances for real-time monitoring of CPU, memory, and processes. Additionally, tools like vmstat, iostat, and sar provide detailed information about system resource usage over time.
What is the purpose of the /etc/fstab file?
The /etc/fstab file is a system configuration file that contains information about filesystems and their mount points. It is used during the system boot process to automatically mount partitions and network shares. The file specifies options like filesystem type, mount point, and mount options
How do you kill a process in Linux?
The kill command is used to terminate processes in Linux. By default, it sends the SIGTERM signal to gracefully terminate a process. You can use the ps command to find the process ID (PID) and then use kill PID to send the termination signal. For more forceful termination, you can use kill -9 PID to send the SIGKILL signal.
What is the purpose of the grep command?
The grep command is used to search for specific patterns or regular expressions within text files or command output. It scans the input and displays lines that match the specified pattern. It can be combined with other commands using pipes (|) to perform advanced text processing operations.
How do you check disk space usage in Linux?
The df command is commonly used to check disk space usage in Linux. It displays information about the filesystems, their mount points, total size, used space, and available space. Adding the h option provides human-readable output with sizes in a more understandable format.
What is a daemon in Linux?
A daemon is a background process that runs continuously and provides specific services in Linux. Daemons are often started during the system boot process and perform various tasks, such as network services (e.g., web server, database server), system monitoring, or scheduled tasks.
How do you create and extract compressed archives in Linux?
Linux provides various tools to create and extract compressed archives. The most commonly used commands are tar, gzip, bzip2, and zip. For example, to create a tar archive and compress it with gzip, you can use tar -czvf archive.tar.gz files. To extract the archive, use tar -xzvf archive.tar.gz.
What is the purpose of the sudo command?
The sudo command is used in Linux to execute commands with administrative privileges. It allows authorized users to perform system tasks or run commands as the root user temporarily. This helps ensure security by restricting access to sensitive operations.
How do you check system logs in Linux?
Linux stores system logs in the /var/log directory. The most common log files include /var/log/syslog, /var/log/messages, and /var/log/auth.log. You can use tools like less or tail to view log files in real-time. Additionally, the journalctl command is used to view systemd journal logs.
Explain the role of the chroot command.
xplain the role of the chroot command. Ans: The chroot command is used to change the apparent root directory for a process and its children. It creates a restricted environment where the specified directory becomes the new root directory. This is often used for security purposes to isolate processes and limit their access to the rest of the filesystem.
How do you check the IP address of a Linux system?
The ip command is commonly used to check the IP address of a Linux system. By running ip addr show or ip a, you can view the network interfaces along with their associated IP addresses. Another command, ifconfig, can also be used, although it is being deprecated in favor of ip command.
What is SSH key authentication in Linux?
SSH key authentication is a secure method of logging into a remote Linux system using cryptographic key pairs. It involves generating a public and private key pair on the local system and adding the public key to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on the remote system. This allows passwordless authentication for SSH connections.

How do you manage user accounts and groups in Linux?
User accounts and groups can be managed using commands like useradd, userdel, usermod, groupadd, groupdel, and groupmod. These commands allow you to create new users, delete users, modify user properties, create new groups, delete groups, and modify group settings.
How do you check the system information in Linux?
The uname command is commonly used to check system information in Linux. By running uname -a, you can view details such as the kernel version, hostname, processor architecture, and operating system.
Explain the purpose of the /etc/resolv.conf file.
The /etc/resolv.conf file is used by Linux systems to configure DNS (Domain Name System) resolution. It specifies the DNS servers that should be used for name resolution. It also defines domain search suffixes and other DNS-related settings.
How do you mount and unmount filesystems in Linux?
The mount command is used to mount filesystems in Linux. By specifying the device or partition to mount and the mount point directory, you can make the filesystem accessible. The umount command is used to unmount filesystems when they are no longer needed.
What is the purpose of the ifconfig command?
The ifconfig command is used to configure and display network interface information in Linux. It allows you to view and modify network interface settings, such as IP addresses, netmasks, and network-related parameters. However, it is being deprecated in favor of the ip command.
How do you check the running processes in Linux?
The ps command is commonly used to check running processes in Linux. By running ps aux or ps -ef, you can view a list of processes along with their process IDs (PIDs), resource utilization, and other details. Adding the grep command can help filter specific processes.
Explain the use of the rsync command.
The rsync command is used for efficient file synchronization and data transfer in Linux. It can be used to copy and synchronize files and directories locally or between different systems over a network. rsync only transfers the differences between files, minimizing data transfer.
What is a runlevel in Linux?
Runlevels in Linux define different system states and configurations. They determine which services and processes should be started or stopped during system startup. Common runlevels include single user mode, multi-user mode, and graphical user mode. The default runlevel is usually defined in the /etc/inittab file.
Explain the purpose of the /etc/passwd file.
The /etc/passwd file is a system file in Linux that stores user account information. Each line in the file represents a user and contains details such as the username, user ID (UID), group ID (GID), home directory, default shell, and more. However, modern Linux systems typically use /etc/shadow for password storage.
How do you check the disk usage of a directory in Linux?
The du command is used to check disk usage in Linux. By running du -sh /path/to/directory, you can view the summarized disk usage of a directory, including its subdirectories. The -s option provides a summary, and the -h option displays the sizes in human-readable format.
How do you find and kill a specific process in Linux?
The pgrep command is commonly used to find processes based on their name or other attributes. Once you have identified the process ID (PID), you can use the kill command with the PID to terminate the process. For example, kill PID or kill -9 PID (forceful termination)
What is the purpose of the cron and crontab files?
The cron and crontab files are used to schedule and automate recurring tasks in Linux. The cron file, located in /etc/cron.d/ or /etc/cron.daily/, contains system-wide cron jobs. The crontab files, accessed using the crontab command, are used to create and manage cron jobs for individual users.
How do you change file permissions in Linux?
The chmod command is used to change file permissions in Linux. You can specify permissions using either symbolic notation (e.g., chmod u+r file) or octal notation (e.g., chmod 644 file). The symbolic notation includes options to grant or revoke permissions for the owner, group, and others.
What is the purpose of the /etc/hosts file?
The /etc/hosts file is a plain-text file that maps hostnames to IP addresses on a local system. It is used to resolve hostnames to IP addresses without the need for DNS (Domain Name System) queries. Users can define custom mappings in this file for local hostname resolution.
How do you check the current directory in Linux?
The pwd command is used to print the current working directory in Linux. By running pwd, it will display the absolute path of the current directory you are in.
Explain the use of the ln command in Linux.
The ln command is used to create links between files or directories in Linux. There are two types of links: hard links and symbolic links (or soft links). Hard links create additional file entries that point to the same data on the disk, while symbolic links are pointers to the target file or directory.


How do you monitor system resource usage in Linux?
Linux provides various tools to monitor system resource usage. Commonly used tools include top, htop, and glances for real-time monitoring of CPU, memory, and processes. Additionally, tools like vmstat, iostat, and sar provide detailed information about system resource usage over time.
What is the purpose of the find command in Linux?
The find command is used to search for files and directories based on various criteria, such as name, size, type, permissions, and more. It allows you to locate files and perform operations on them, such as copying, moving, or deleting. The find command is highly flexible and powerful.
How do you check the system uptime in Linux?
The uptime command is used to check the system uptime in Linux. By running uptime, it will display the current time, how long the system has been running, the number of logged-in users, and the system load average over different time intervals.
Explain the use of the iptables command in Linux.
The iptables command is used to configure and manage the netfilter firewall in Linux. It allows you to set up rules for filtering network traffic, performing Network Address Translation (NAT), and implementing packet manipulation. iptables is a powerful tool for network security and traffic control.
How do you check the size of a directory and its contents in Linux?
The du command is commonly used to check the size of a directory and its contents in Linux. By running du -sh directory, it will display the summarized disk usage of the specified directory, including all its subdirectories. The -s option provides a summary, and the -h option displays sizes in a human-readable format.
What is the purpose of the chown command in Linux?
The chown command is used to change the ownership of files and directories in Linux. It allows you to modify the user and/or group ownership of a file or directory. The ownership can be specified using the username, group name, or their corresponding numeric IDs.


How do you check the available memory in Linux?
The free command is commonly used to check the available memory in Linux. By running free -h, it will display information about the system’s total memory, used memory, free memory, and other memory-related statistics. The -h option displays sizes in a human-readable format.
What is a shebang in Linux?
A shebang, also known as a hashbang, is a line at the beginning of a script file that specifies the interpreter to be used for executing the script. It typically starts with #! followed by the path to the interpreter. For example, #!/bin/bash specifies that the script should be executed using the Bash shell.
How do you check the listening ports in Linux?
The netstat command is commonly used to check the listening ports in Linux. By running netstat -tuln, it will display a list of all open ports and the corresponding services or processes that are listening on those ports. The -t option filters TCP ports, -u filters UDP ports, -l lists only listening sockets, and -n displays port numbers instead of service names.
What is the purpose of the /etc/shadow file in Linux?
The /etc/shadow file is a system file that stores encrypted user passwords in Linux. It provides an additional layer of security by keeping the password hashes separate from the /etc/passwd file. Only privileged users can access the /etc/shadow file.
How do you create a symbolic link in Linux?
The ln command is used to create symbolic links (also known as soft links) in Linux. By running ln s target link_name, it will create a symbolic link named link_name that points to the target file or directory. Symbolic links are references to the target, not actual copies.
What is a Linux distribution, and what are some examples?
A Linux distribution is a version of the Linux operating system that includes a specific set of software and tools. Examples include Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian.
How do you create a new user in Linux? How do you grant that user sudo privileges?
To create a new user, use the adduser command followed by the username. To grant sudo privileges to a user, add the user to the sudo group using the usermod command.
How do you list the contents of a directory, and how do you recursively list the contents of subdirectories?
To list the contents of a directory, use the ls command. To recursively list the contents of subdirectories, use the ls -R command.
How do you search for a file by name, and how do you search for a string within the contents of a file?
To search for a file by name, use the find command. To search for a string within the contents of a file, use the grep command.
How do you set environment variables in Linux, and how do you temporarily set environment variables for a single command?
To set environment variables in Linux, you can use the export command. To temporarily set environment variables for a single command, you can use the env command.

How do you schedule a task to run automatically in Linux using cron?
To schedule a task to run automatically in Linux using cron, you can use the crontab command to open the crontab file and add a new entry specifying the schedule and command to be run.
How do you view and kill running processes in Linux, and how do you view log files?
To view running processes in Linux, use the ps command. To kill a process, use the kill command followed by the process ID. To view log files, you can use a text editor or the tail command to view the end of a log file.
What is Linux and How it is different from Windows ?
Linux is free and open source Operating System and it is Multi User operating System developed by Linux Torvalds Windows OS developed by Microsoft and it is single user operating system developed by Microsoft.
What is Linux Distribution
As linux is free and open source Operating system, many companies has taken linux source code and modified according to their requirement and released into market. Those releases are called as Linux Distributions. Ex: Amazon Linux, Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat Linux, SUSE etc




Can you explain Linux Architecture
Applications -> Shell -> Kernel -> Hardware
What is Linux Loader ?
LILO (Linux Loader) is basically a bootloader for Linux that is used to load Linux into memory and start the OS.
What is Kernel? Explain its functions.
A kernel is considered the main component of Linux OS. It is simply a resource manager that acts as a bridge between hardware and software. Its main role is to manage hardware resources for users and is generally used to provide an interface for user-level interaction. A kernel is the first program that is loaded whenever a computer system starts. It is also referred to as low-level system software. Its other main functions include:
- Memory Management
- Process Management
- Device Management
- Storage Management
- Manage access, and use of various peripherals that are connected to the computer.
What is BASH?
BASH (Bourne Again Shell) is basically a command language interpreter. It was written by Brian Fox for GNU OS and can be used in place of Bourne Shell. It is similar to Bourne Shell but includes some additional features such as command-line editing that make it easier and more convenient to use. It is the default user shell on most Linux installations. It is basically an interpreted and non-compiled process that can also run in the terminal window. It is also capable of reading commands from shell scripts
What is swap space?
Swap space, as the name suggests, is basically a space on a hard disk that is used when the amount of physical memory or RAM is full. It is considered a substitute for physical memory. Its main function is to substitute disk space for RAM memory when real RAM does not have enough space to hold all programs that are executing, and more space is required. In simple words, it can be used as an extension of RAM by Linux.
What is Vi Editor ?
VI editor (Visual Editor) is basically a default text editor that usually comes with most of the Linux OS. There are basically three types of modes used in VI editor as given below:
- Command Mode/Regular Mode:
- Insertion Mode/Edit Mode:
- Ex Mode/Replacement Mode:
What are file permissions in Linux? Name different types of file systems in Linux.
There are three owners in the Linux System i.e., user, group, and others. These owners have three types of permissions defined as listed below:
- Read (r): It allows the user to open and read the file or list the directory.
- Write (w): It allows the user to open and modify the file. One can also add new files to the directory.
- Execute (x): It allows the user to execute or run the file. One can also lookup a specific file within a directory
What is a Zombie Process?
Zombie Process, also referred to as a defunct or dead process in Linux, is a process that has finished the execution, but its entry remains in the process table. It usually happens due to a lack of correspondence between parent and child processes. This process occurs for the child process because the parent process needs to read the status of the child process. Once it is completed using the wait system call, this process is removed from the process table.
what is awk command ?
The awk command is a versatile text processing tool commonly found on Unix-like operating systems. It takes input from files or standard input and performs various operations on it, such as searching for specific patterns, extracting and manipulating data, and generating reports. The basic syntax of the awk command is as follows: $ awk options 'pattern { action }' input_file
How to delete 2 months old files in Linux Machine ?
To delete files that are two months old on a Linux machine, you can use a combination of the find command and the rm command. Here's an example command you can use: $ find /path/to/directory -type f -mtime +60 -exec rm {} \;
You need to transfer files securely between two Linux servers. How would you set up and configure an encrypted SSH connection to ensure secure file transfers?
To securely transfer files between two Linux servers, you can set up and configure an encrypted SSH connection using the Secure Copy (SCP). $ ssh-copy-id
How to check free space in Linux ?
To check the free space on a Linux system, you can use the df command (short for “disk free”)
How to check Linux version ?
To check the Linux version, you can use the lsb_release command or the uname command
How to display all users belongs to a group in Linux ?
To display all the users belonging to a specific group in Linux, you can use the getent command $ getent group <groupname>
Which Linux machines are using in your project?
RHEL Based Linux Machines We are using in our project.



How do you iterate over a list of items in a shell script?
You can iterate over a list of items using a for loop. For example:
for item in item1 item2 item3
do
echo $item
Done
How do you define and use functions in a shell script?
Functions can be defined in a shell script using the function keyword or simply by defining a block of code. For example:
function greet {
echo "Hello, $1!"
}
greet "John"
This will output "Hello, John!".
How do you check if a directory exists in a shell script?
You can check the existence of a directory using the -d flag with the test or [ command. For example, [ -d directory ] will return true if the directory "directory" exists.
How can you redirect the output of a command to a file?
The output of a command can be redirected to a file using the > operator. For example, ls > file.txt will redirect the output of the ls command to the file "file.txt".
How do you handle errors or exceptions in a shell script?
Errors or exceptions in a shell script can be handled using the trap command to set up a signal handler. This allows you to catch and handle specific signals or errors. Additionally, you can use conditional statements like if-else to handle errors based on exit codes or specific condition
How can you pass the output of one command as an argument to another command?
The output of one command can be passed as an argument to another command using command substitution with the $() syntax. For example, command2 $(command1) will pass the output of command1 as an argument to command2.
How do you compare strings in a shell script?
String comparison can be done using conditional statements such as if-else and the test or [ command. For example, [ "$str1" = "$str2" ] checks if str1 is equal to str2.
How can you get the length of a string in a shell script?
The length of a string can be obtained using the ${#string} syntax. For example, length=${#str} will store the length of the string str in the variable length.
How do you check if a variable is empty in a shell script?
You can check if a variable is empty using conditional statements. For example, [ -z "$var" ] will return true if the variable var is empty.
How do you perform arithmetic operations in a shell script?
Arithmetic operations can be performed using the expr command or by using the $((...)) syntax. For example, result=$((num1 + num2)) will store the sum of num1 and num2 in the variable result.
How do you read lines from a file in a shell script?
Lines can be read from a file using the while loop combined with the read command. For example:
while read line
do
echo $line
done < file.t

You have reached the end of the blog!
Devops Multi cloud Training
Choose the training style that fits your schedule — Self-Paced or Live Interactive Sessions. Both include hands-on projects, expert support, and lifetime access.
| Feature | Self-Paced Training | Live Training |
|---|---|---|
| 🎯 Mode | 🎥Pre-Recorded Session | 🧑🏫Live Class + Recordings |
| 💼 Projects | 🕒 Weekend Real-Time Projects | 📅 Weekdays + Weekend Real-Time Projects |
| ❓ Doubt Clearing | 📞 Weekend Live Support Session | 🧠 Anytime Doubt Clearing Session |
| 👥 Career Support & Mentorship | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| 🎓 Global Certification Training | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| 🔑 Access | ♾️ Lifetime Access | ♾️ Lifetime Access |
| 💰 Fees | ₹4,999 (2 x ₹2,500) | ₹7,999 (2 x ₹4,000) |
| ℹ️ For More Info | Explore Self-Paced Training | Explore Live Training |

